A classic Andre Weil-tale is his narrow escape from being shot as a Russian spy
The war was a disaster for Weil who was a conscientious objector and so wished to avoid military service. He fled to Finland, to visit Rolf Nevanlinna, as soon as war was declared. This was an attempt to avoid being forced into the army, but it was not a simple matter to escape from the war in Europe at this time. Weil was arrested in Finland and when letters in Russian were found in his room (they were actually from Pontryagin describing mathematical research) things looked pretty black. One day Nevanlinna was told that they were about to execute Weil as a spy, and he was able to persuade the authorities to deport Weil instead.
 However, Weil’s wikipedia entry calls this a story too good to be true, and continues
However, Weil’s wikipedia entry calls this a story too good to be true, and continues
In 1992, the Finnish mathematician Osmo Pekonen went to the archives to check the facts. Based on the documents, he established that Weil was not really going to be shot, even if he was under arrest, and that Nevanlinna probably didn’t do – and didn’t need to do – anything to save him. Pekonen published a paper on this with an afterword by Andre Weil himself. Nevanlinna’s motivation for concocting such a story of himself as the rescuer of a famous Jewish mathematician probably was the fact that he had been a Nazi sympathizer during the war. The story also appears in Nevanlinna’s autobiography, published in Finnish, but the dates don’t match with real events at all. It is true, however, that Nevanlinna housed Weil in the summer of 1939 at his summer residence Korkee at Lohja in Finland – and offered Hitler’s Mein Kampf as bedside reading.
This old spy-story gets a recent twist now that it turns out that Weil’s descent theory of tori has applications to cryptography. So far, I haven’t really defined what tori are, so let us start with some basics.
The simplest (and archetypical) example of an algebraic torus is the multiplicative group(scheme) $\mathbb{G}_m $ over a finite field $\mathbb{F}_q $ which is the affine variety
$\mathbb{V}(xy-1) \subset \mathbb{A}^2_{\mathbb{F}_q} $. that is, the $\mathbb{F}_q $ points of $\mathbb{G}_m $ are precisely the couples ${ (x,\frac{1}{x})~:~x \in \mathbb{F}_q^* } $ and so are in one-to-one correspondence with the non-zero elements of $\mathbb{F}_q $. The coordinate ring of this variety is the ring of Laurant polynomials $\mathbb{F}_q[x,x^{-1}] $ and the fact that multiplication induces a group-structure on the points of the variety can be rephrased by saying that this coordinate ring is a Hopf algebra which is just the Hopf structure on the group-algebra $\mathbb{F}_q[\mathbb{Z}] = \mathbb{F}_q[x,x^{-1}] $. This is the first indication of a connection between tori defined over $\mathbb{F}_q $ and lattices (that is free $\mathbb{Z} $-modules with an action of the Galois group $Gal(\overline{F}_q/F_q) $. In this correspondence, the multiplicative group scheme $\mathbb{G}_m $ corresponds to $\mathbb{Z} $ with the trivial action.
Now take a field extension $\mathbb{F}_q \subset \mathbb{F}_{q^n} $, is there an affine variety, defined over $\mathbb{F}_q $ whose $\mathbb{F}_q $-points are precisely the invertible elements $\mathbb{F}_{q^n}^* $? Sure! Just take the multiplicative group over $\mathbb{F}_{q^n} $ and write the elements x and y as $x = x_1 + x_2 a_2 + \ldots + x_n a_n $ (and a similar expression for y with ${ 1,a_2,\ldots,a_n }$ being a basis of $\mathbb{F}_{q^n}/\mathbb{F}_q $ and write the defning equation $xy-1 $ out, also with respect to this basis and this will then give you the equations of the desired variety, which is usually denoted by $R^1_{\mathbb{F}_{q^n}/\mathbb{F}_q} \mathbb{G}_m $ and called the Weil restriction of scalars torus.
A concrete example? Take $\mathbb{F}_9 = \mathbb{F}_3(\sqrt{-1}) $ and write $x=x_1+x_2 \sqrt{-1} $ and $y=y_1+y_2 \sqrt{-1} $, then the defining equation $xy-1 $ becomes
$~(x_1y_1-x_2y_2) + (x_1y_2-x_2y_1) \sqrt{-1} = 1 $
whence $R^1_{\mathbb{F}_9/\mathbb{F}_3} = \mathbb{V}(x_1y_1-x_2y_2-1,x_1y_2-x_2y_1) \subset \mathbb{A}^4_{\mathbb{F}_3} $, the intersection of two quadratic hypersurfaces in 4-dimensional space.
Why do we call $R^1 \mathbb{G}_m $ a _torus_? Well, as with any variety defined over $\mathbb{F}_q $ we can also look at its points over a field-extension, for example over the algebraic closure $\overline{\mathbb{F}}_q $ and then it is easy to see that
$R^1_{\mathbb{F}_{q^n}/\mathbb{F}_q} \mathbb{G}_m (\overline{\mathbb{F}}_q) = \overline{\mathbb{F}}_q^* \times \ldots \times \overline{\mathbb{F}}_q^* $ (n copies)
and such algebraic groups are called tori. (To understand terminology, the compact group corresponding to $\mathbb{C}^* \times \mathbb{C}^* $ is $U_1 \times U_1 = S^1 \times S^1 $, so a torus).
In fact, it is already the case that the $\mathbb{F}_{q^n} $ points of the restriction of scalar torus are $\mathbb{F}_{q^n}^* \times \ldots \times \mathbb{F}_{q^n}^* $ and therefore we call this field a splitting field of the torus.
This is the general definition of an algebraic torus : a torus T over $\mathbb{F}_q $ is an affine group scheme over $\mathbb{F}_q $ such that, if we extend scalars to the algebraic closure (and then it already holds for a finite extension) we get an isomorphism of affine group schemes
$T \times_{\mathbb{F}_q} \overline{\mathbb{F}}_q = \overline{\mathbb{F}}_q^* \times \ldots \times \overline{\mathbb{F}}_q^* = (\overline{\mathbb{F}}_q^*)^{n} $
in which case we call T a torus of dimension n. Clearly, the Galois group $Gal(\overline{\mathbb{F}}_q^*/\mathbb{F}_q) $ acts on the left hand side in such a way that we recover $T $ as the orbit space for this action.
Hence, anther way to phrase this is to say that an algebraic torus is the Weil descent of an action of the Galois group on the algebraic group $\overline{\mathbb{F}}_q^* \times \ldots \times \overline{\mathbb{F}}_q^* $.
Of course we can also rephrase this is more algebraic terms by looking at the coordinate rings. The coordinate ring of the algebraic group $~(\overline{\mathbb{F}}_q^*)^n $ is the group-algebra of the rank n lattice $\mathbb{Z}^n = \mathbb{Z} \oplus \ldots \oplus \mathbb{Z} $ (the free Abelian group of rank n), that is,
$\overline{\mathbb{F}}_q [ \mathbb{Z}^n ] $. Now the Galois group acts both on the field $\overline{\mathbb{F}}_q $ as on the lattice $\mathbb{Z}^n $ coming from the action of the Galois group on the extended torus $T \times_{\mathbb{F}_q} \overline{\mathbb{F}}_q $. In fact, it is best to denote this specific action on $\mathbb{Z}^n $ by $T^* $ and call $T^* $ the character group of $T $. Now, we recover the coordinate ring of the $\mathbb{F}_q $-torus $T $ as the ring of invariants
$\mathbb{F}_q[T] = \overline{\mathbb{F}}_q [T^*]^{Gal(\overline{\mathbb{F}}_q/\mathbb{F}_q)} $
Hence, the restriction of scalars torus $R^1_{\mathbb{F}_{q^n}/\mathbb{F}_q} \mathbb{G}_m $ is an n-dimensional torus over $\mathbb{F}_q $ and its corresponding character group is the free Abelian group of rank n which can be written as $\mathbb{Z}[x]/(x^n-1) = \mathbb{Z}1 \oplus \mathbb{Z}x \oplus \ldots \oplus \mathbb{Z}x^{n-1} $ and where the action of the cyclic Galois group $Gal(\mathbb{F}_{q^n}/\mathbb{F}_q) = C_n = \langle \sigma \rangle $ s such that the generator $\sigma $ as as multiplication by $x $. That is, in this case the character group is a permutation lattice meaning that the $\mathbb{Z} $-module has a basis which is permuted under the action of the Galois group. Next time we will encounter more difficult tori sich as the crypto-torus $T_n $.
Leave a Comment
 Another combinatorial gadget assigned to the fundamental domain is the
Another combinatorial gadget assigned to the fundamental domain is the 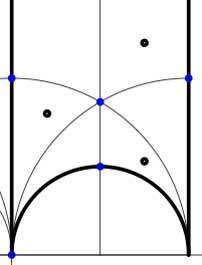
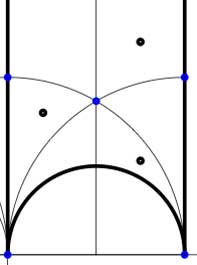 In these cases the fundamental domain consists of 6 triangles with the indicated vertices (the blue dots). The distinction between the two is that in the first case, one identifies the two edges of the left, resp. bottom, resp. right boundary (so, in particular, 0,1 and $\infty $ are identified) whereas in the second one identifies the two edges of the left boundary and identifies the edges of the bottom with those of the right boundary (here, 0 is identified only with $\infty $ but also $1+i $ is indetified with $\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{2}i $).
In these cases the fundamental domain consists of 6 triangles with the indicated vertices (the blue dots). The distinction between the two is that in the first case, one identifies the two edges of the left, resp. bottom, resp. right boundary (so, in particular, 0,1 and $\infty $ are identified) whereas in the second one identifies the two edges of the left boundary and identifies the edges of the bottom with those of the right boundary (here, 0 is identified only with $\infty $ but also $1+i $ is indetified with $\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{2}i $).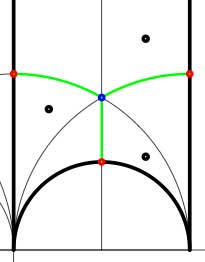 In both cases the dessin seems to be the same (and given by the picture on the right). However, in the first case all three red vertices are distinct hence there are no internal red vertices in this case whereas in the second case we should identify the bottom and right-hand red vertex which then becomes an internal red vertex of the dessin!
In both cases the dessin seems to be the same (and given by the picture on the right). However, in the first case all three red vertices are distinct hence there are no internal red vertices in this case whereas in the second case we should identify the bottom and right-hand red vertex which then becomes an internal red vertex of the dessin!