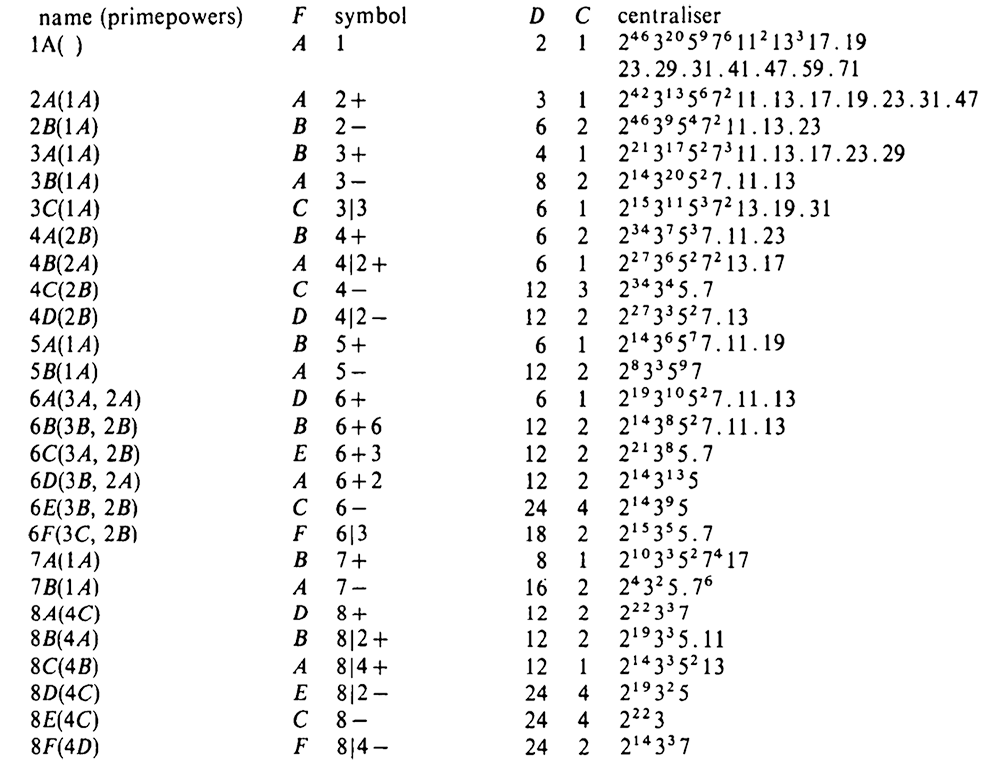
At a seminar at the College de France in 1975, Tits wrote down the order of the monster group
\[
\# \mathbb{M} = 2^{46}.3^{20}.5^9.7^6.11^2.13^3.17·19·23·29·31·41·47·59·71 \]
Andrew Ogg, who attended the talk, noticed that the prime divisors are precisely the primes $p$ for which the characteristic $p$ super-singular $j$-invariants are all defined over $\mathbb{F}_p$.
Here’s Ogg’s paper on this: Automorphismes de courbes modulaires, Séminaire Delange-Pisot-Poitou. Théorie des nombres, tome 16, no 1 (1974-1975).
Ogg offered a bottle of Jack Daniels for an explanation of this coincidence.
Even Richard Borcherds didn’t claim the bottle of Jack Daniels, though his proof of the monstrous moonshine conjecture is believed to be the best explanation, at present.
A few years ago, John Duncan and Ken Ono posted a paper “The Jack Daniels Problem”, in which they prove that monstrous moonshine implies that if $p$ is not one of Ogg’s primes it cannot be a divisor of $\# \mathbb{M}$. However, the other implication remains mysterious.
Duncan and Ono say:
“This discussion does not prove that every $p ∈ \text{Ogg}$ divides $\# \mathbb{M}$. It merely explains how the first principles of moonshine suggest this implication. Monstrous moonshine is the proof. Does this then provide a completely satisfactory solution to Ogg’s problem? Maybe or maybe not. Perhaps someone will one day furnish a map from the characteristic $p$ supersingular $j$-invariants to elements of order $p$ where the group structure of $\mathbb{M}$ is apparent.”
I don’t know whether they claimed the bottle, anyway.
But then, what is the non-commutative Jack Daniels Problem?
A footnote on the first page of Conway and Norton’s ‘Monstrous Moonshine’ paper says:
“Very recently, A. Pizer has shown these primes are the only ones that satisfy a certain conjecture of Hecke from 1936 relating modular forms of weight $2$ to quaternion algebra theta-series.”
Pizer’s paper is “A note on a conjecture of Hecke”.
Maybe there’s a connection between monstrous moonshine and the arithmetic of integral quaternion algebras. Some hints:
The commutation relations in the Big Picture are reminiscent of the meta-commutation relations for Hurwitz quaternions, originally due to Conway in his booklet on Quaternions and Octonions.
The fact that the $p$-tree in the Big Picture has valency $p+1$ comes from the fact that the Brauer-Severi of $M_2(\mathbb{F}_p)$ is $\mathbb{P}^1_{\mathbb{F}_p}$. In fact, the Big Picture should be related to the Brauer-Severi scheme of $M_2(\mathbb{Z})$.
Then, there’s Jorge Plazas claiming that Connes-Marcolli’s $GL_2$-system might be related to moonshine.
One of the first things I’ll do when I return is to run to the library and get our copy of Shimura’s ‘Introduction to the arithmetic theory of automorphic functions’.
Btw. the bottle in the title image is not a Jack Daniels but the remains of a bottle of Ricard, because I’m still in the French mountains.
Comments closed